Zinc
Zinc, with symbol Zn, is the 23rd more abundant element amongst the elements of the earth crust. It doesn’t exist as free element in nature, and it can be extracted from many minerals. The most common form is to find it as Zinc Sulphide (ZnS) in Zinc blends. The richest reserves contain almost a 10% of Iron and between 40-50% of Zinc.
Main applications of Zinc are:
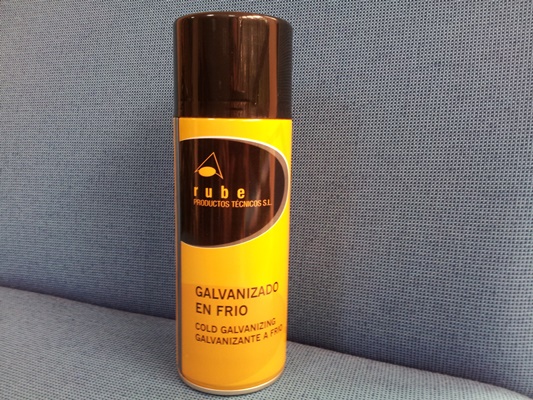
Galvanization. Almost 50% of annual consumption is for Steel galvanizing, to protect it from corrosion, protection which is effective even when the covering is cracked because Zinc acts as a sacrifice anode.
Batteries of ZN-AgO. It is used in aerospace industry due to its optimal performance per unit of weight and in batteries Zinc-air for laptops.
Foundry. Zinc and alloys for manufacturing of foundry pieces for automotive industry. Zinc Oxide. Chemical compound used as an accelerator and activator for rubber vulcanization. It acts as a protecting pigment against UV radiation in paints and inks. It is also used in Pharmaceutical industry and animal/ human feeding.